Unplugged Python: Creative Review Activities for the New School Year
Unplugged activities are great for back-to-school sessions as they help ease students back into learning while fostering collaboration and problem-solving skills. Here are some unplugged Python review activities tailored for high school students:
1. Python Keywords and Syntax Relay Race
- Objective: Review basic Python keywords and syntax.
- Setup: Create cards with Python keywords, operators, or syntax rules (e.g., `if`, `else`, `for`, `while`, `==`, `!=`, etc.).
- Activity: Divide students into teams. Each team must match the correct keyword to a description or write a correct Python statement using a provided keyword. The first team to correctly match or write all their statements wins.
2. Algorithm Storytelling
- Objective: Reinforce logical thinking and algorithm design.
- Setup: Provide students with a problem to solve (e.g., finding the largest number in a list, sorting a list of items).
- Activity: Students work in small groups to write out the steps (algorithm) on paper or a whiteboard as if they were instructing someone who doesn’t know Python. They must ensure the steps are clear, logical, and precise.
3. Python Function Puzzle
- Objective: Review function definitions, parameters, and return values.
- Setup: Prepare puzzle pieces where each piece contains a part of a Python function (e.g., function name, parameters, body, return statement).
- Activity: Students work individually or in pairs to assemble the puzzle pieces correctly, creating a valid Python function.
4. Python Code Debugging Posters
- Objective: Practice identifying and fixing errors in Python code.
- Setup: Create posters with short Python code snippets that contain common errors (syntax errors, logic errors, etc.).
- Activity: Hang the posters around the classroom. Students rotate in groups, identifying and correcting the errors on each poster. After all groups have rotated, discuss the corrections as a class.
Posters samples:
Here are some examples of Python code snippets containing common errors that can be turned into posters for classroom display. Each poster should include the code snippet, a brief explanation of the error, and space for students to write the correct version of the code.
Poster 1: Syntax Error - Missing Colon
Snippet:
if x > 10
print("x is greater than 10")Error Explanation:
This code snippet is missing a colon (:) at the end of the if statement, which is required for the syntax to be correct.
Space for Correction:
______________________
Poster 2: Logic Error - Off-By-One in Loop
Snippet:
for i in range(1, 10):
print(i)Error Explanation:
This loop will print numbers from 1 to 9, not including 10. The logic might be incorrect if the intention was to include 10.
Space for Correction:
_______________________
Poster 3: Syntax Error - Mismatched Parentheses
Snippet:
total = sum(1, 2, 3, 4))Error Explanation:
There’s an extra closing parenthesis in this code, causing a syntax error.
Space for Correction:
______________________
Poster 4: Logic Error - Incorrect Use of == for Assignment
Snippet:
if x = 5:
print("x is 5")Error Explanation:
The = operator is used for assignment, not comparison. To compare values, use ==.
Space for Correction:
______________________
Poster 5: Syntax Error - Indentation
Snippet:
def greet(name):
print("Hello, " + name)Error Explanation:
The print statement is not indented, which will result in an IndentationError.
Space for Correction:
____________________
Poster 6: Logic Error - Incorrect Boolean Logic
Snippet:
if age > 18 and age < 30:
print("You are eligible.")Error Explanation:
This logic checks if the age is between 18 and 30 but does not include 18 and 30. This might be incorrect depending on the intention.
Space for Correction:
_____________________
Poster 7: Syntax Error - Missing Quotation Marks
Snippet:
print("Hello, world!)Error Explanation:
The closing quotation mark is missing, which will cause a syntax error.
Space for Correction:
________________________
Poster 8: Logic Error - Unintentional Infinite Loop
Snippet:
while x > 0:
print(x)Error Explanation:
If x is not modified within the loop, this will result in an infinite loop.
Space for Correction:
_____________________
5. Conditional Statements Sorting Game
- Objective: Review if-else and elif structures.
- Setup: Prepare cards with different conditional statements and corresponding actions.
- Activity: Students sort the cards into correct if-else or elif sequences, matching conditions with the appropriate actions. This can be turned into a competition to see who finishes first.
6. Data Types Charades
- Objective: Reinforce understanding of Python data types (e.g., strings, integers, lists).
- Setup: Write different data types and examples (e.g., `[1, 2, 3]`, `"Hello"`, `42`) on cards.
- Activity: Students take turns acting out or describing the data type without saying the type itself, while others guess the correct data type.
7. Flowchart to Code Conversion
- Objective: Translate logical flowcharts into Python code.
- Setup: Provide students with flowcharts that represent simple algorithms or processes.
- Activity: In groups, students discuss and write out the Python code that would follow the logic of the flowchart. They can compare their answers with another group afterward.
Flowcharts samples:
1. Flowchart for a Simple "if-else" Decision
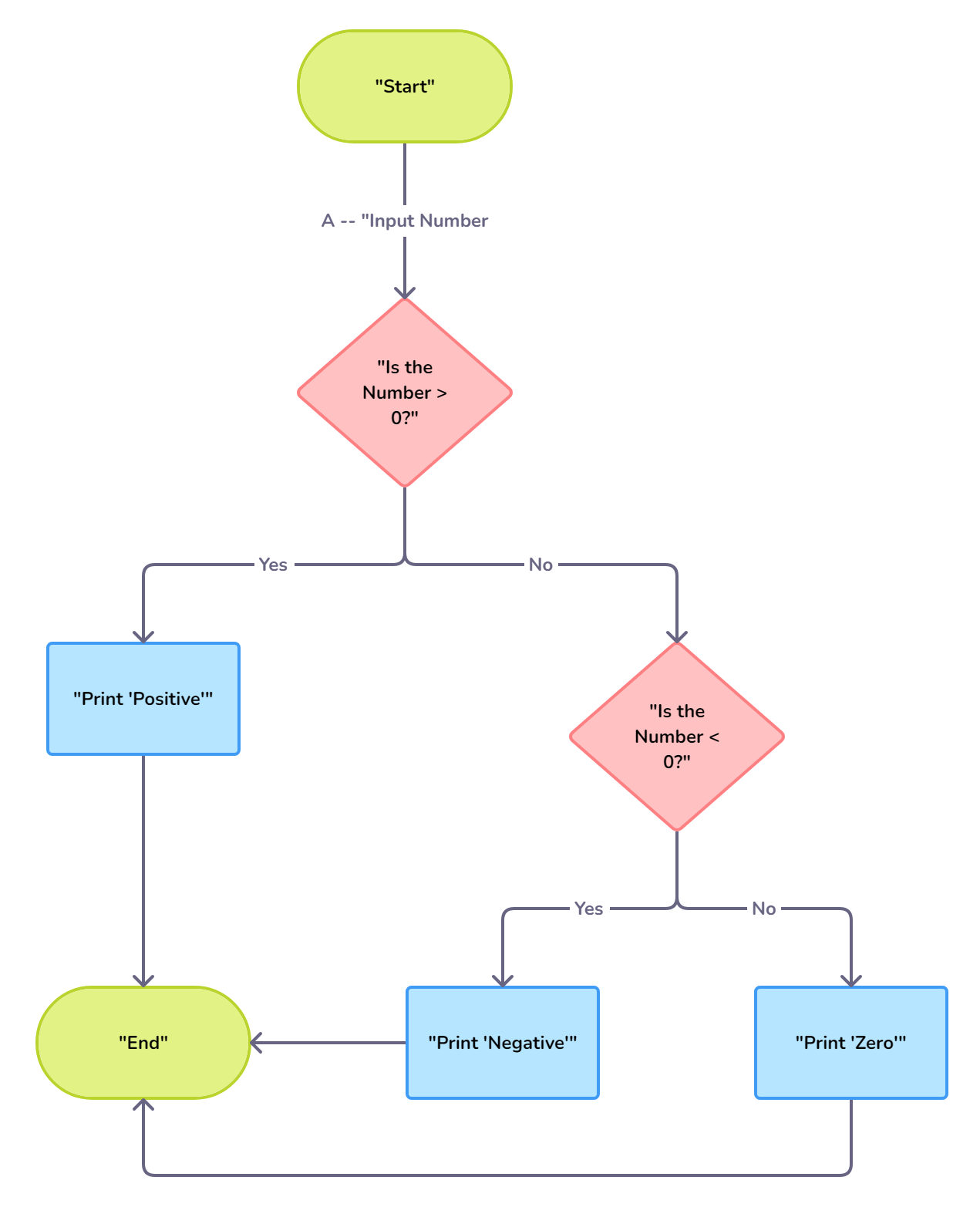
- Purpose: To demonstrate a basic decision-making process.
- Scenario: Checking if a number is positive, negative, or zero.
Flowchart:
- Start
- Input Number
- Is the Number > 0?
- Yes: Print "Positive"
- No: Move to the next decision
- Is the Number < 0?
- Yes: Print "Negative"
- No: Print "Zero"
5. End
2. Flowchart for a Simple "for" Loop
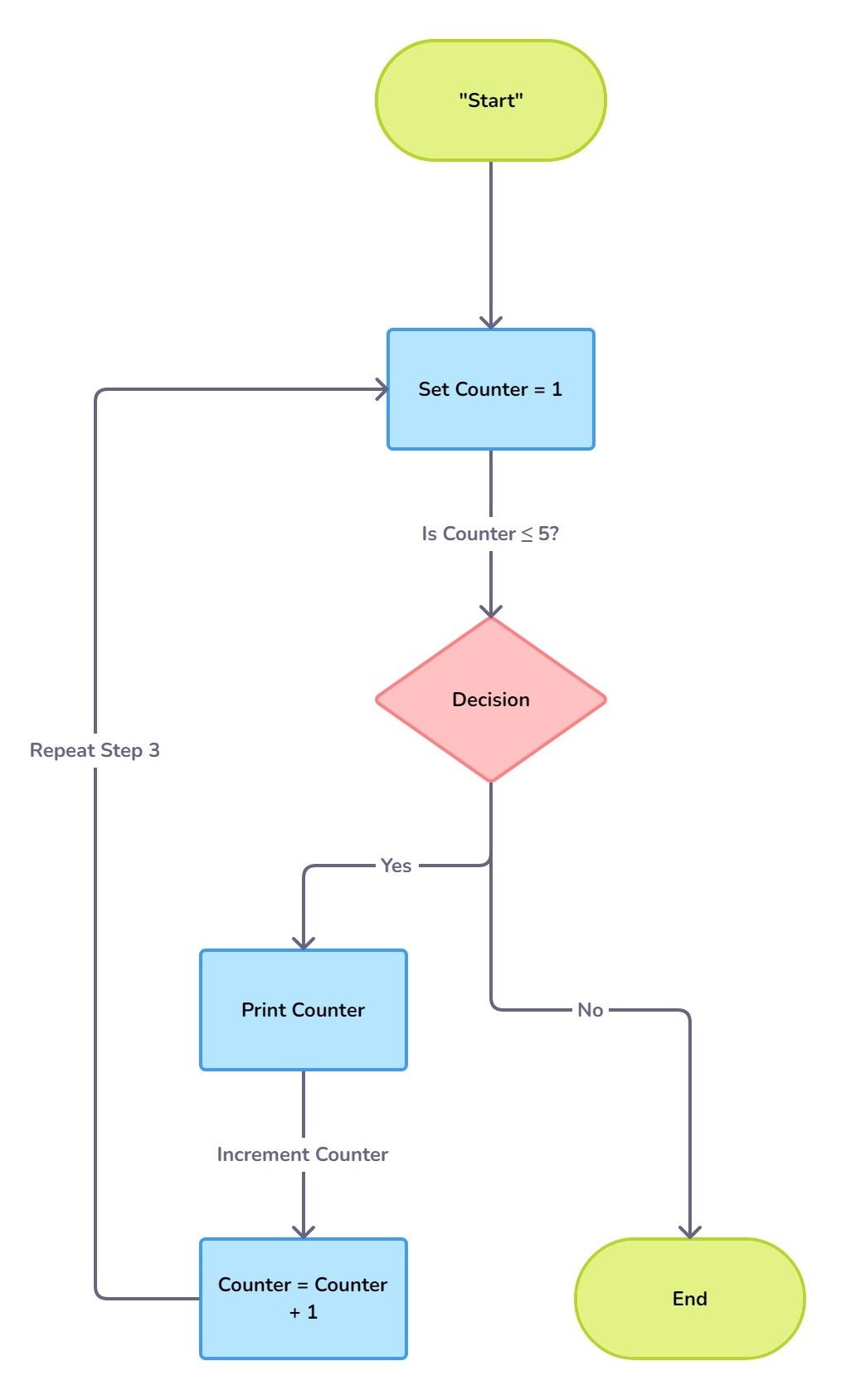
- Purpose: To illustrate the use of a loop.
- Scenario: Printing numbers from 1 to 5.
Flowchart:
1. Start
2. Set Counter = 1
3. Is Counter ≤ 5?
- Yes: Print Counter
- No: Move to End
4. Increment Counter by 1
5. Repeat Step 3
6. End
3. Flowchart for a Basic Function Call
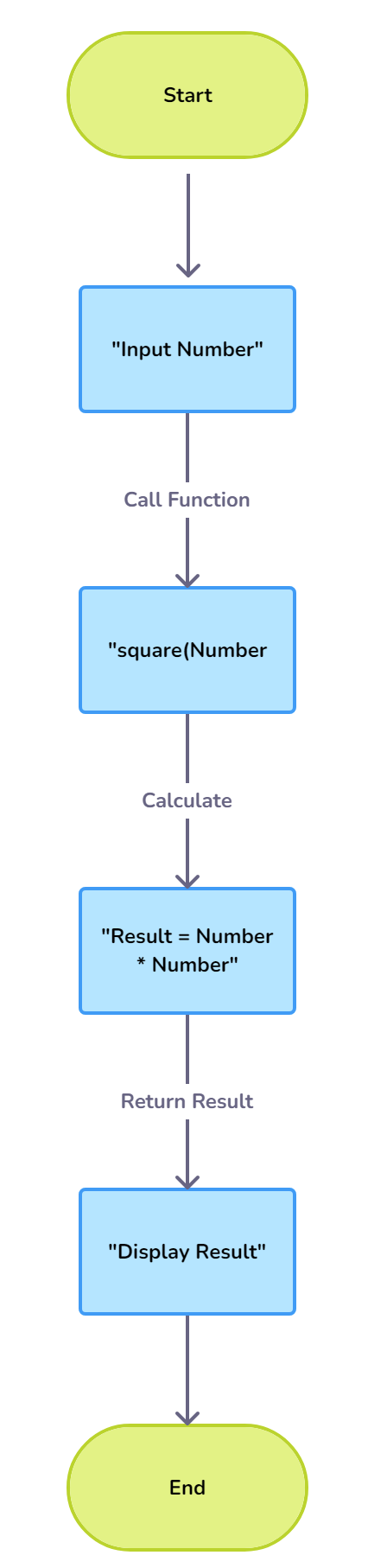
- Purpose: To show how a function is called and returns a value.
- Scenario: Calculating the square of a number.
Flowchart:
1. Start
2. Input Number
3. Call Function "square(Number)"
- Inside Function:
- Calculate: "Result = Number * Number"
- Return Result
4. Display Result
5. End
______
4. Flowchart for a Simple "while" Loop
- Purpose: To explain a loop that continues based on a condition.
- Scenario: Keep doubling a number until it exceeds 100.
Flowchart:
1. Start
2. Input Number
3. Is Number ≤ 100?
- Yes: Double the Number (Number = Number * 2)
- No: Move to End
4. Repeat Step 3
5. End
_____
5. Flowchart for Finding the Maximum of Two Numbers
- Purpose: To demonstrate the process of comparing two values.
- Scenario: Comparing two numbers to find the larger one.
Flowchart:
1. Start
2. Input Number1 and Number2
3. Is Number1 > Number2?
- Yes: Print "Number1 is Larger"
- No: Print "Number2 is Larger"
4. End
6. Flowchart for Checking if a Number is Even or Odd
- Purpose: To illustrate the modulus operation and condition checking.
- Scenario: Determining if a number is even or odd.
Flowchart:
1. Start
2. Input Number
3. Is Number % 2 == 0?
- Yes: Print "Even"
- No: Print "Odd"
4. End
___________
8. Python Code Scavenger Hunt
- Objective: Review and identify correct Python syntax.
- Setup: Hide small snippets of Python code around the classroom.
- Activity: Give students a list of specific code elements (e.g., a for loop, a print statement, a variable assignment). Students must find and collect the code snippets that match the list, assembling them into a complete program at the end.
9. Human Python Interpreter
- Objective: Help students understand how Python code is executed step-by-step.
- Setup:
- Prepare simple Python programs on paper (e.g., looping through a list, using if-else conditions).
- Activity:
- Select a few students to be "variables," "operators," and "control structures."
- The rest of the class "runs" the program by giving commands, and the "variables" and "operators" act out their roles.
- Discussion: Reflect on how the code was executed and any errors encountered during the role play.
10. Python Circuit Game
- Objective: Practice Python syntax and logical flow in a physical game.
- Setup:
- Set up stations around the classroom, each representing a different part of a Python program (e.g., "Input," "Loop," "Condition," "Output").
- Activity:
- Students move from station to station, writing a part of the code or solving a problem at each station.
- The final station combines all parts into a complete Python program.
- Discussion: Review the program as a class, discussing how each part contributes to the final result.
11. Python Concept Speed-Dating
- Objective: Rapidly review a variety of Python concepts in a fun, interactive way.
- Setup:
- Set up pairs of chairs around the room. On each chair, place a card with a Python concept or code snippet.
- Activity:
- Students pair up, sit in the chairs, and discuss the concept or code snippet on the card for a set amount of time (e.g., 2 minutes).
- After time is up, one student rotates to the next chair, and the process repeats.
- Discussion: After several rounds, debrief on any challenging concepts and clarify misunderstandings.
12. Python Paradox Puzzle - Objective: Challenge students with logical puzzles that require Python concepts to solve.
- Setup:
- Prepare paradox puzzles or brainteasers that involve Python concepts (e.g., “Write a program that prints numbers from 1 to 100, but for multiples of 3 print 'Fizz' instead of the number, and for multiples of 5 print 'Buzz'. For numbers which are multiples of both three and five, print 'FizzBuzz'”).
- Activity:
- Students solve these puzzles on paper, discussing their reasoning and the code they would write.
- Discussion: Share solutions and different approaches to the puzzles.
13. Python Code Escape Room - Objective: Use Python knowledge to solve puzzles and "escape" from the room.
- Setup:
- Create a series of puzzles that involve Python concepts like loops, conditionals, and functions.
- Each puzzle leads to a clue for the next one, culminating in a final code or key to "escape."
- Activity:
- Students work in teams to solve the puzzles and progress through the "escape room."
- Discussion: Review the solutions and the Python concepts behind each puzzle.
14. Python Logic Board Game - Objective: Reinforce Python logic and problem-solving through a board game.
- Setup:
- Design a board game where each space requires solving a Python-related challenge to move forward (e.g., debugging a code snippet, writing a short function).
- Activity:
- Students play the game in small groups, helping each other solve the challenges to advance on the board.
- Discussion: After the game, discuss the challenges they encountered and how they solved them.
15. Python Code Poetry
- Objective: Combine creativity with coding by writing Python code in poetic form.
- Setup:
- Introduce the concept of "code poetry," where students write Python code that is functional but also structured like a poem.
- Activity:
- Students create their own code poems, using loops, conditionals, and other Python structures in a creative way.
- Example: A loop that prints lines of a poem or a function that generates random poetic verses.
- Discussion: Share the poems and discuss how Python can be used creatively.
16. Python Function Fashion Show - Objective: Make learning about functions fun by having students "model" their function creations.
- Setup:
- Have students create a Python function that performs a specific task (e.g., generating a pattern, solving a small problem).
- Activity:
- Students present their functions in a "fashion show" format, explaining what their function does and why it's useful.
- Discussion: Highlight interesting or unique functions and discuss their applications.
17. Python Concept Bingo
- Objective: Review a variety of Python concepts in a game format.
- Setup:
- Create bingo cards with Python keywords, functions, or concepts instead of numbers.
- Activity:
- Call out definitions or descriptions, and students mark the corresponding concept on their bingo cards.
- The first to get a bingo wins, but keep playing to review all the concepts.
- Discussion: Review the concepts that were covered, clarifying any that caused confusion.
18. Python Reverse Coding Challenge
- Objective: Strengthen problem-solving skills by working backwards from the output to the code.
- Setup:
- Provide students with an output result and challenge them to write the Python code that would produce that result.
- Activity:
- Students work individually or in pairs to write code that matches the given output.
- Example: "The output is 10, 8, 6, 4, 2. Write the code that produces this sequence."
- Discussion: Share the different approaches students took and discuss which ones were the most efficient or elegant.
19. Python Code Comics - Objective: Combine creativity with coding concepts by creating comic strips that explain Python concepts.
- Setup:
- Provide templates or blank sheets for students to create comic strips. Each strip should represent a Python concept (e.g., loops, conditionals).
- Activity:
- Students draw and write comic strips that explain the concept in a humorous or engaging way. For example, a comic about a loop might show a character stuck in a repeating task until a condition is met.
- Discussion: Share the comics with the class and discuss how well they explain the concepts.
20. Python Vocabulary Crossword - Objective: Reinforce Python terminology and concepts through a crossword puzzle.
- Setup:
- Create a crossword puzzle with clues related to Python keywords, functions, and concepts (e.g., "The keyword used to define a function").
- Activity:
- Students work individually or in pairs to complete the crossword. Consider offering a small prize for the first correct completion.
- Discussion: Review the answers as a class, providing explanations for any terms that were challenging.
These activities provide a variety of ways to review Python concepts, combining creativity, physical activity, and problem-solving in an unplugged setting.


